IMAGING CYCLER
Imaging Cycler® basic
a cost-effective 4-in-one microscope
It combines:
- Conventional multichannel fluorescence LED microscopy
- Super-resolution (<40nm) of structures and multi-protein networks (specific tag-libraries)
- >100 molecular parameter imaging at 2D in one cell or tissue section, one visual field
- >100 molecular parameter imaging at 3D in one cell or tissue section, one visual field
Optional: many visual fields.
The Imaging Cycler® TIS™ -HTS-Live
a 6-in-one microscope.
- Conventional multichannel fluorescence microscopy, optional LED-multichannel
- Super-resolution (<40nm) of structures and multi-protein networks (specific tag-libraries)
- >100 molecular parameter imaging at 2D in one cell or tissue section, many visual fields
- >100 molecular parameter imaging at 3D in one cell or tissue section, many visual fields
- Live cell imaging (optional)
- High-throughput screening (HTS) (optional)
For note: Both Imaging Cycler®-basic and Imaging Cycler® TIS™ -HTS-Live are fully automated microscopes that can be also used in conventional non-automated modes for routine daily microscopic analyses as well as for pre-programmed protein network (toponome) imaging. Imaging Cycler® comes with remote control.
Functional super-resolution
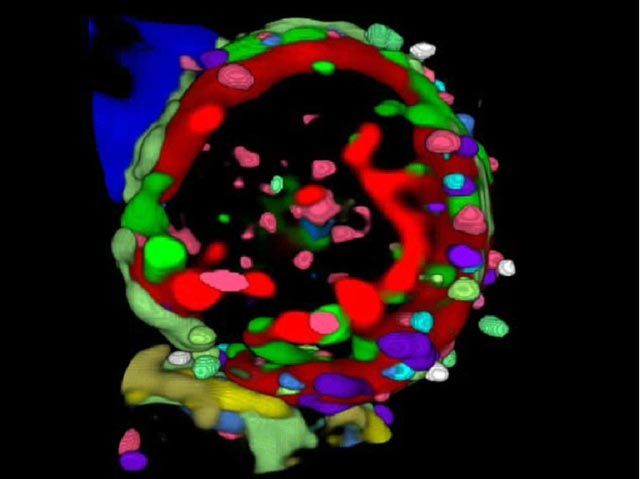
Imaging Cycler® 3D functional super-resolution of interlocked multi-protein clusters at the cell surface of a human blood T lymhocyte. Note: Colours denote the differential assembly of 27 distinct co-mapped membrane proteins ( = protein colocation and anti-colocation code). (after: Friedenberger M et al: Nat Protoc 2007, 2, 2285-84, Schubert W. et al. N Biotechnol 2012)
Simultaneous functional super-resolution of protein networks and super-resolution of structures
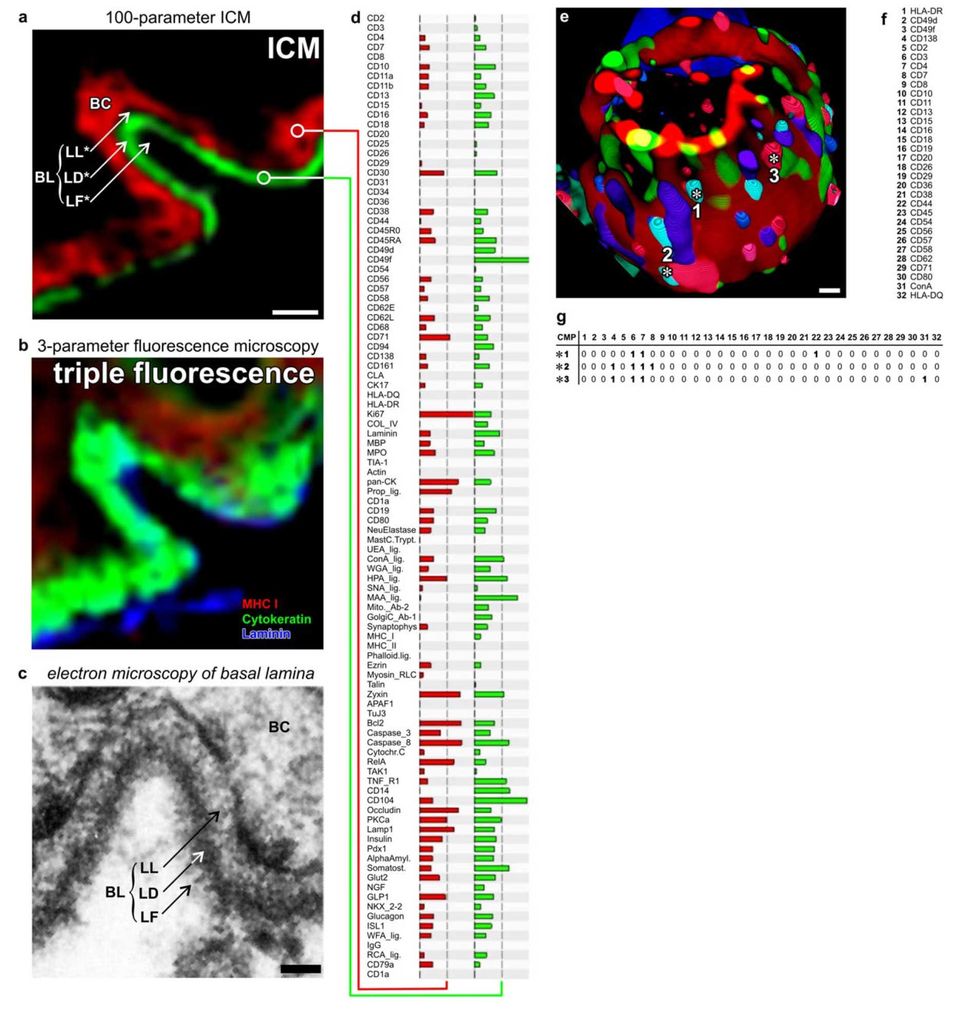
Functional super resolution of large molecular networks. (a-d) Dermoepithelial junction in human tissue. Imaging cycler microscopy based discovery of molecular networks in situ. (a) Direct realtime protein profiling in 100-dimensional ICM data set using an algorithm based on the similarity mapping approach. Each data point has a PCMD of 256100. Note: sharp images at the junctional area discriminating between Lamina Fibroreticularis (LF), Lamina Densa (LD, green profile in d), Lamina Lucida (LL) and the basal ceratinocyte layer (BC, red profile in d), as known from transmission electron microscopy (c). (b) Same area as in (a), displaying traditional triple fluorescence imaging. (e) 3-dimensinal ICM imaging of distinct 32-component multi protein complexes on the cell surface of a blood T- lymphocyte. Multi protein complexes are composed of differential combination of 32 proteins/glycotopes listed in (f). (g) Examples are marked with asterisks (number 1 to 3) and detailed as CMPs with proteins present (1) or absent (0) together characterised as individual CMPs.
Bars: 10 mm (a, b), 50 nm (c), 1 mm (e).
(after: Schubert, W. Life-Saving Microscopy Method for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Cytometry A 2020; 97: 866–868 20/ Schubert W. Advances in toponomics drug discovery: Imaging cycler microscopy correctly predicts a therapy method of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cytometry A 2015;87(8):696-703. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.22671/ Schubert W et al. N Biotechnol 2012/).
Bars: 10 mm (a, b), 50 nm (c), 1 mm (e).
(after: Schubert, W. Life-Saving Microscopy Method for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Cytometry A 2020; 97: 866–868 20/ Schubert W. Advances in toponomics drug discovery: Imaging cycler microscopy correctly predicts a therapy method of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cytometry A 2015;87(8):696-703. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.22671/ Schubert W et al. N Biotechnol 2012/).